Everything You Need to Know About Viral Diseases in Animals

Viral diseases in animals can significantly impact livestock, pets, and wildlife. These diseases, associated with one virus or another, can run through animal herds and flocks, cause illness and death, and decrease production. To prevent such occurrences, people must be educated on the various viral diseases affecting animals and how they can be prevented.
Here, we will examine some of the major viral diseases in animals, their characteristics, life cycles, and possible cures. This guide will be useful for people working in the livestock industry, for those who have pets, and for anyone interested in methods to prevent viral sickness in animals.
What Are Viral Diseases in Animals?
Viral diseases are conditions under which viruses enter the body tissues of animals and cause an infection. They get inside the animal cells, reproduce, and move from cell to cell and from one animal to another. It should be noted that viral diseases can often become an epidemic, primarily if the animals are located in an enclosed area such as farms or kennels for dogs. Some viruses are zoonoses and thus can be transmitted from animals to people, a factor that is important in both animal and public health.
Types of Viral Diseases in Animals
Various kinds of viruses affect different kinds of animals, and the treatment and prevention methods are also different in most cases. Some of the most common animal diseases caused by viruses affect cattle, poultry, dogs, cats, and other domesticated animals.
Cattle Viral Diseases
Some of the potential viral diseases that affect cattle are known to have severe negative impacts on the general health of the animals and also lead to financial losses among the farmers. These cattle viral diseases may be transmitted through direct contact, through water and feed, and even through the bites of insects. Some of the most common cattle viral diseases include:
- Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD): An infectious disease common amongst cattle, pigs, and sheep, among other animals, including those with a cloven hoof. It leads to fever, lesions, and limping in affected animals.
- Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD): An infectious disease that causes diarrhea, respiratory ailments, and conception loss or low efficiency in cattle. Acute and chronic BVD can be identified, and the disease is contagious in that it spreads through contact with infected animals.
- Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR): This cow viral disease is a respiratory disease of cattle that may cause severe pneumonia in affected animals, particularly the young ones.
- Bluetongue Disease: This virus is transmitted through biting insects and is apparent in cattle. It causes fever, swelling, and bluish discoloration of the tongue.
Poultry Viral Diseases
Chickens and turkeys are also susceptible to many viral diseases. These poultry viral diseases are highly contagious among flocks and result in huge losses in egg production and the quality of the end product, meat. Some of the most common poultry viral diseases include:
- Newcastle Disease: This is an acute contagious disease that is passed among chickens. Some of the signs are dyspnoea, paralysis, and sudden death. It is one of the world’s most severe poultry viral diseases today.
- Avian Influenza: Also known as bird flu, this viral infection primarily impacts birds’ respiratory and digestive systems. It can cause severe illness and death in infected poultry.
- Marek’s Disease: This viral disease infects chickens and results in tumors and paralysis. It is carried in the dust and dander in poultry houses and affects the poultry birds.
Infectious Bronchitis: This poultry viral disease affects the respiratory system of chickens and, in severe cases, can cause poor laying, coughs, and sneezing.
Cow Viral Diseases
Besides the cattle viral diseases common in large groups of cows, certain diseases affect individual cows and can have serious repercussions. They are diseases that may negatively affect a cow’s productivity, reproductive health, and general well-being. Some of the common cow viral diseases are:
- Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV): This virus tends to infect cows’ lungs, triggering respiratory distress and causing difficulty breathing again. It is especially dangerous to young calves.
- Bovine Leukemia Virus (BLV): BLV leads to leukemia in cows, and some of its effects include the formation of tumors in Lymph nodes, weight loss, and reduced milk production.
- Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1): This virus leads to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis and can also cause abortion in pregnant cows.
Other Viral Diseases in Animals
Besides cattle viral diseases and poultry viral diseases, almost all animals, such as dogs, cats, sheep, goats, and horses, are susceptible to viral diseases. Some common viral diseases in animals include:
- Rabies: A highly fatal viral illness in the nervous system of animals such as dogs and cats. The disease is affected by the enzootic bite of a sick animal.
- Canine Parvovirus: This virus infects dogs, and its symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, and severe dehydration, particularly in young dogs.
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV): This viral infection compromises cats’ immune responses, making them vulnerable to other diseases and infections.
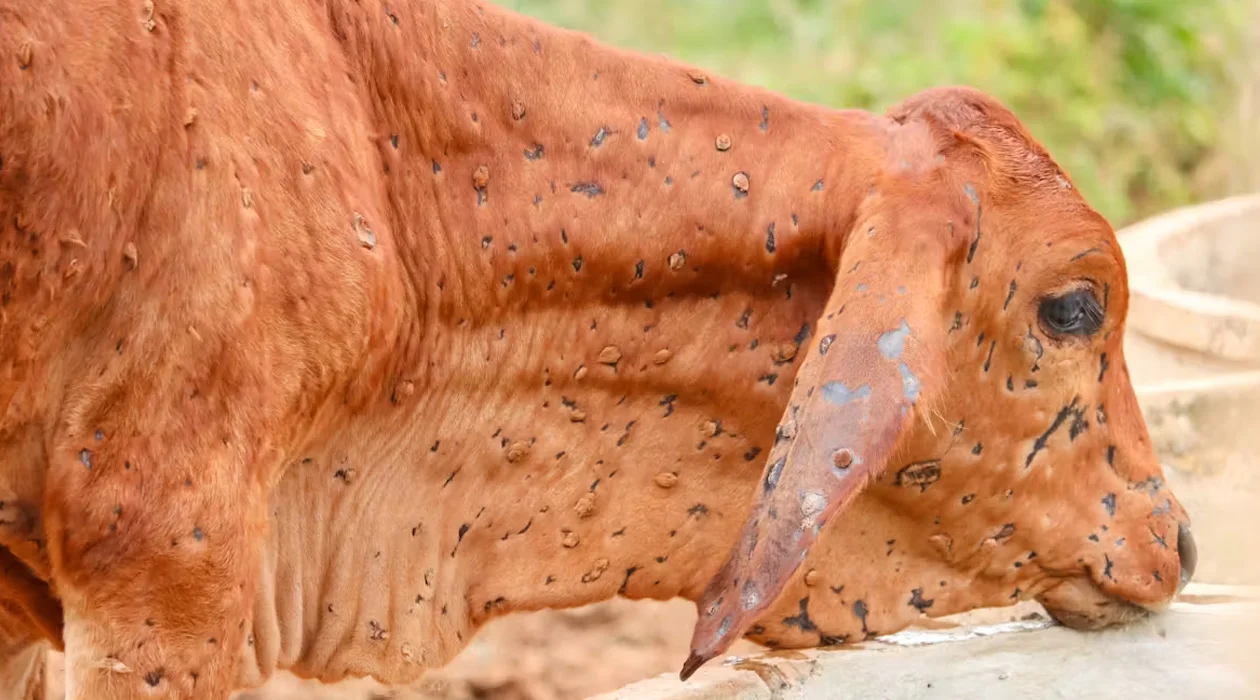

How to Prevent and Treat Viral Diseases in Animals
Animal viral diseases should be controlled through general hygienic practices, immunization, and prevention of ADB. Here are some essential tips to help protect animals from viral infections:
Vaccination
Vaccination is one measure that can be adopted to control viral diseases in animals. Vaccines assist the immune system in becoming familiar with a particular virus in relation to the disease. Vaccinations are important and necessary for livestock and our pets so that they cannot be affected by various viral diseases, such as cattle, cows, and poultry.
Hygiene and Biosecurity
To reduce virus spread, farms, kennels, and poultry houses must implement appropriate hygiene and cleanliness measures. Measures such as avoiding direct contact with infected animals, taking appropriate measures to treat water sources, and not intermingling infected animals with healthy ones can effectively reduce the occurrence of the aforementioned crude disease risks. To reduce the incidence of viral diseases in animals, new animals must be isolated before incorporating them into the existing stock.
Treatment Options
Although prevention is the best measure to keep off the diseases, some diseases affect animals and need treatment when they show signs. Many viral animal diseases can be treated using veterinary remedies such as antiviral products and other additional treatment options. Further, herbal solutions and homeopathy treatments are becoming preferred as more and more animal owners seek treatments that would positively affect animals without causing severe side effects, as those often seen in ordinary anti-inflammatories.
About Goel Vet Pharma
Goel Vet Pharma incorporated a new way of veterinary homeopathy in the historical city of CHITTORGARH. We mainly offer homeopathic remedies for animal ailments such as cattle viral disease, cow viral disease, poultry viral disease, and many others. Our products are designed to treat animals naturally and healthy without harming them. At Goel Vet Pharma, we are dedicated to providing good-quality Veterinary homeopathic medicines for Cattle, Buffalo, Sheep, Goats, Dogs, and Cats.
Importance of Monitoring and Early Detection
Viral diseases can be easily spread from animals; thus, it is crucial to identify and follow the diseases in animals early. Farmers and pet owners should be careful and watch for such signs in their animals as they may indicate illness. Cough, sneezing, high fever, vomiting and diarrhea, and loss of appetite should not be taken lightly and should be treated as early as possible. Early detection is one of the critical factors that can ensure a reduction in the contamination rate of viral diseases.
Conclusion
Viral animal diseases are catastrophic to livestock, pets, and wildlife. Learning more about the causes, signs, and management of some of the most prevalent sicknesses in animals is crucial to preventing any diseases. Vaccination, hygiene practices, and diagnosis at an early stage play an integral role in managing cattle viral diseases, cow viral diseases, and poultry viral diseases.
You can find natural homeopathic products at Goel Vet Pharma that safely treat animals’ health. Therefore, taking appropriate precautions and consulting qualified veterinarians where necessary can avoid the devastating ramifications of animal viral infections.
 Australian Shepherd
Australian Shepherd Beagle
Beagle Belgium Shepherd
Belgium Shepherd Bernese Mountain Dog
Bernese Mountain Dog Border Collie
Border Collie Boxer
Boxer Bulldog
Bulldog Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Chihuahua
Chihuahua Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniel Dachshund
Dachshund Doberman Pinscher
Doberman Pinscher Dogo Argentino
Dogo Argentino French Bulldog
French Bulldog German Shepherd
German Shepherd Golden Retriever
Golden Retriever Great Dane
Great Dane Himalayan Shepherd
Himalayan Shepherd Indie Dogs
Indie Dogs Labrador Retriever
Labrador Retriever Pakistani Bully
Pakistani Bully Pembroke Welsh Corgi
Pembroke Welsh Corgi Pitbull
Pitbull Pomeranian
Pomeranian Poodle
Poodle Pug
Pug Rottweiler
Rottweiler Shih Tzu
Shih Tzu Siberian Husky
Siberian Husky Yorkshire Terrier
Yorkshire Terrier Abyssinian
Abyssinian American Bobtail
American Bobtail American Shorthair
American Shorthair Balinese Cat
Balinese Cat Bengal Cat
Bengal Cat Birman
Birman Bombay Cat
Bombay Cat British Longhair
British Longhair British Shorthair
British Shorthair Burmese Cat
Burmese Cat Devon Rex
Devon Rex Exotic Shorthair
Exotic Shorthair Himalayan Cat
Himalayan Cat Maine Coon
Maine Coon Oriental Shorthair
Oriental Shorthair Persian Cats
Persian Cats Ragdoll
Ragdoll Scottish Fold
Scottish Fold Siamese Cat
Siamese Cat Siberian Cat
Siberian Cat Sphynx Cat
Sphynx Cat