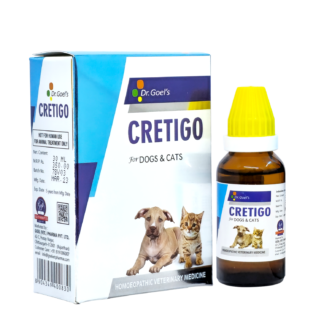
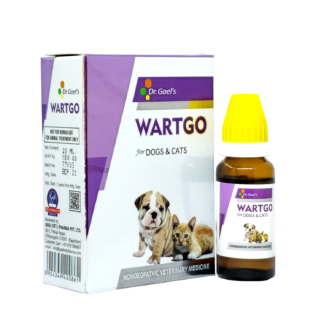
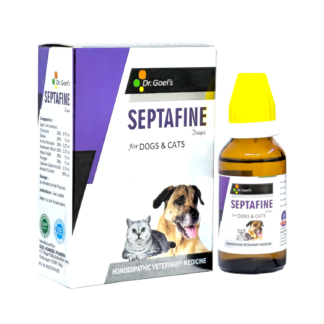
PayDay Sale ALERT: 25% Off on Pet Food
- Home
- Shop by BreedDogCatDog
 Australian Shepherd
Australian Shepherd Beagle
Beagle Belgium Shepherd
Belgium Shepherd Bernese Mountain Dog
Bernese Mountain Dog Border Collie
Border Collie Boxer
Boxer Bulldog
Bulldog Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Chihuahua
Chihuahua Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniel Dachshund
Dachshund Doberman Pinscher
Doberman Pinscher Dogo Argentino
Dogo Argentino French Bulldog
French Bulldog German Shepherd
German Shepherd Golden Retriever
Golden Retriever Great Dane
Great Dane Himalayan Shepherd
Himalayan Shepherd Indie Dogs
Indie Dogs Labrador Retriever
Labrador Retriever Pakistani Bully
Pakistani Bully Pembroke Welsh Corgi
Pembroke Welsh Corgi Pitbull
Pitbull Pomeranian
Pomeranian Poodle
Poodle Pug
Pug Rottweiler
Rottweiler Shih Tzu
Shih Tzu Siberian Husky
Siberian Husky Yorkshire Terrier
Yorkshire Terrier
Cat - Shop by Diseases
- Shop by Products
- Blogs
- Consult a Vet
- About us
- Update
- Home
- Shop by BreedDogCatDog
 Australian Shepherd
Australian Shepherd Beagle
Beagle Belgium Shepherd
Belgium Shepherd Bernese Mountain Dog
Bernese Mountain Dog Border Collie
Border Collie Boxer
Boxer Bulldog
Bulldog Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Chihuahua
Chihuahua Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniel Dachshund
Dachshund Doberman Pinscher
Doberman Pinscher Dogo Argentino
Dogo Argentino French Bulldog
French Bulldog German Shepherd
German Shepherd Golden Retriever
Golden Retriever Great Dane
Great Dane Himalayan Shepherd
Himalayan Shepherd Indie Dogs
Indie Dogs Labrador Retriever
Labrador Retriever Pakistani Bully
Pakistani Bully Pembroke Welsh Corgi
Pembroke Welsh Corgi Pitbull
Pitbull Pomeranian
Pomeranian Poodle
Poodle Pug
Pug Rottweiler
Rottweiler Shih Tzu
Shih Tzu Siberian Husky
Siberian Husky Yorkshire Terrier
Yorkshire Terrier
Cat - Shop by Diseases
- Shop by Products
- Blogs
- Consult a Vet
- About us
- Update
 Abyssinian
Abyssinian American Bobtail
American Bobtail American Shorthair
American Shorthair Balinese Cat
Balinese Cat Bengal Cat
Bengal Cat Birman
Birman Bombay Cat
Bombay Cat British Longhair
British Longhair British Shorthair
British Shorthair Burmese Cat
Burmese Cat Devon Rex
Devon Rex Exotic Shorthair
Exotic Shorthair Himalayan Cat
Himalayan Cat Maine Coon
Maine Coon Oriental Shorthair
Oriental Shorthair Persian Cats
Persian Cats Ragdoll
Ragdoll Scottish Fold
Scottish Fold Siamese Cat
Siamese Cat Siberian Cat
Siberian Cat Sphynx Cat
Sphynx Cat