The Ultimate Guide to Essential Pet Grooming Products
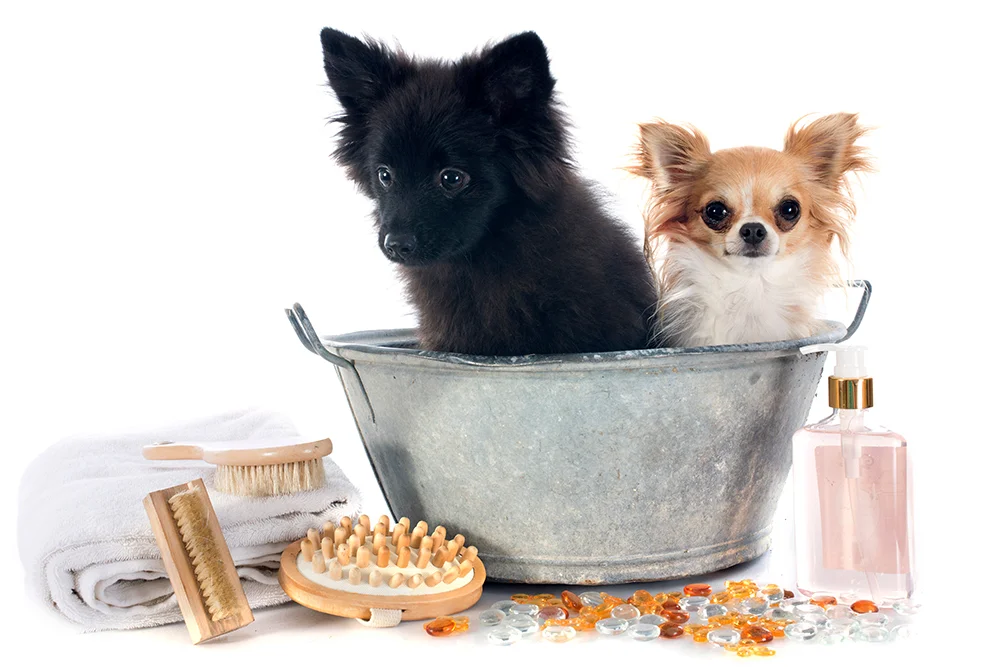

Our pets’ cleanliness and overall living conditions go hand in hand with hygiene, which is a crucial element of every grooming style. Bathing and brushing as part of a pet’s grooming routine can be done using the right pet grooming supplies, and it prevents skin issues and excessive shedding. Whether you are experienced in caring for a pet or planning to find a suitable grooming solution for your new pet, this guide will provide you with essential information to make the right choice regarding pet grooming products for your loved pet.
Choosing the Right Grooming Products for Your Pet
The first thing that one needs to do is to know the requirements of his or her pet animal to choose the right grooming products. Coats vary with breed, length, and density, and some may shed copiously while others are non-shedding. Here’s a breakdown of some factors to consider:
- Coat Type: Whether it is short or long, curly or straight, there are specific coats and, therefore, tools needed for each. The type of coat will also depend on it. Short-coated pets may only require the deshedding brush, while long-coated pets may require two brushes: entangling and managing the fur coat.
- Skin Sensitivity: Some animals have very sensitive skin, specifically on the ears, and they should not be given shampoo that can cause irritation. Seek products with mild skin types specifically suited for those with sensitive skin.
- Shedding: Frequent shedding usually requires lots of brushing and effective tools to remove the fur left behind in the house.
- Lifestyle: Pets that are playful and enjoy being outdoors may require frequent washing, while those that are kept indoors with little exposure to dirt and dust may require washing less often.
Essential Pet Grooming Products: A Checklist
Now that you understand your pet’s individual needs let’s explore the essential pet grooming products you’ll need to keep your furry friend looking and feeling their best:
- Brushes and Combs
- Slicker Brush: This brush is perfect for daily grooming, fetching loose hair and avoiding tangles, especially for medium—and long-haired animals.
- Deshedding Brush: Effectively eliminates loose undercoat and helps regulate shedding in short, long, and double-coated breeds.
- Undercoat Rake: This product penetrates the undercoat and helps to remove dead hair while bathing, reducing shedding and enhancing skin health.
- Comb: Ideal for untangling tough knots and clearing clogs in all kinds of coats of your pet.
- Shampoos and Conditioners
- Shampoo: Select a shampoo appropriate for your pet’s type of coat and any skin conditions it might have. Opt for hypo-allergic products.
- Conditioner (Optional): Conditioners help maintain the fur texture and are most beneficial for a breed with long fur.
- Nail Clippers and Trimmers
- By maintaining short nails, one does not have to deal with discomfort, possible injuries, or furniture destruction. When selecting clippers or trimmers, ensure that they are suitable for your pet based on its size and paw shape.
- Ear Cleaners and Wipes
- This prevents ear infections and irritation, common in those with naturally dirty ears. Wash the ears with a non-irritant cleaner designed for animals to avoid causing discomfort to your pet.
- Ear Wipes: These are especially suitable for ‘top-up’ cleaning and for removing debris from your pet’s ears.
- Other Useful Products
- Grooming Wipes: These are very convenient for in-between bath cleaning, for example, for paws and faces.
- Detangling Spray: A detangling spray is used before brushing the hair to soften the knots and mats and ease the grooming process.
- Dental Care Products: This involves washing your pet’s teeth so that they do not develop dental complications in the future. Dental chews, toothpaste, and a toothbrush specially intended for pets are ideal for this process.
- Towels: Microfiber towels are very soft and can quickly dry your pet without stressing the fur.
Building Your Pet Grooming Kit
Given the number of grooming products available out there, it becomes quite challenging to decide on which one to use. Here’s how to build a basic pet grooming kit tailored to your pet’s needs:
- Start with the essentials: A sponge, soap, conditioner (if needed), nail cutter, and ear drops or cleaner are some of the basic tools that need to be carried along when grooming pets.
- Upgrade as needed: Depending on your pet’s coat type or the grooming required, you can add features like an undercoat or a deshedding brush.
- Consider a pre-assembled kit: Pet stores offer various types of grooming equipment in sets. Depending on your pet and its coat type, specific kits are available.
Making Grooming Time a Positive Experience for Your Pet
Now that you have the right pet grooming products, here are some tips for a successful grooming experience:
- Create a positive association: During these grooming sessions, it is advisable to use only pleasant methods, such as treats, praise, and gentle touches.
- Groom regularly: Pet owners must take a few minutes of their time and brush their pet at least 2 to 3 times a week to control shedding, eliminate matting, and promote a healthy coat.
- Bathing frequency: Overall, the frequency of baths depends on your pet’s activity level and coat type. Please seek advice from your veterinarian.
- Focus on sensitive areas: It is advisable to be gentle when washing or trimming the sensitive parts of the dog’s body, such as the face, legs, and ears.
- Use proper techniques: Learn the correct brushing practices and nail trimming procedures to protect your pet from injuries.
Use Proper Techniques to Avoid Discomforting Your Pet
Proper handling of a pet involves using certain grooming products, which is important to avoid causing discomfort to the pet. Here are some specific points to keep in mind:
- Brushing: When brushing, follow the lay of the fur, starting at the head and then down the whole body length. Remember to be as soft as possible while brushing, and never pull the hair off the animal’s body. However, if you come across a mat, spray some water or apply a detangling spray or conditioner to ease the mat before brushing.
- Bathing: Always rinse your pet using warm water and a mild shampoo suitable for the breed of its fur. Try not to let the shampoo get into their eyes and ears. Rinse the hair well to eliminate all shampoo deposits.
- Nail Trimming: Slip under the skin the quick area of the pink colour of the nail, which contains blood capillaries and nerves. Do not make incisions with the knife blade since this will be painful, and a lot of blood will result. If you have any issues in clipping your pet’s nails, then seeking the services of a groomer or your vet is best.
- Ear Cleaning: Do not use human cleaning products for your pet; use special ear cleaners meant for pets. Mix the solution with water and apply this to a cotton ball, then clean your pet’s outer ear using this. Do not attempt to push the cotton ball right into the ear canal.
Additional Considerations for Effective Pet Grooming
- Desensitization: Desensitization measures would come in handy if your pet becomes agitated at the sight of grooming tools. First, acquaint them with the grooming equipment and allow them to associate it only with treats and compliments. Depending on their response, try to extend the amount of time each session to groom your pet.
- Professional Grooming: Some pets may require professional grooming, especially those with difficult fur or dense undercoat. Expert groomers use the right tools and skills to address specific issues and thoroughly groom your pet in a stress-free process.
Conclusion
Pet grooming is not limited to washing pets; it is an important cultural practice that should be done properly with the right pet grooming products. It’s great fun for both the dog and the owner, allows for the detection of any health issues, and teaches you about treating your pet. You should assess your pet’s grooming requirements, select the right equipment and apply the correct methods so you and your loved companion will have a pleasant grooming experience. So always keep in mind that a clean animal is a healthy animal!
 Australian Shepherd
Australian Shepherd Beagle
Beagle Belgium Shepherd
Belgium Shepherd Bernese Mountain Dog
Bernese Mountain Dog Border Collie
Border Collie Boxer
Boxer Bulldog
Bulldog Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Cavalier King Charles Spaniel Chihuahua
Chihuahua Cocker Spaniel
Cocker Spaniel Dachshund
Dachshund Doberman Pinscher
Doberman Pinscher Dogo Argentino
Dogo Argentino French Bulldog
French Bulldog German Shepherd
German Shepherd Golden Retriever
Golden Retriever Great Dane
Great Dane Himalayan Shepherd
Himalayan Shepherd Indie Dogs
Indie Dogs Labrador Retriever
Labrador Retriever Pakistani Bully
Pakistani Bully Pembroke Welsh Corgi
Pembroke Welsh Corgi Pitbull
Pitbull Pomeranian
Pomeranian Poodle
Poodle Pug
Pug Rottweiler
Rottweiler Shih Tzu
Shih Tzu Siberian Husky
Siberian Husky Yorkshire Terrier
Yorkshire Terrier Abyssinian
Abyssinian American Bobtail
American Bobtail American Shorthair
American Shorthair Balinese Cat
Balinese Cat Bengal Cat
Bengal Cat Birman
Birman Bombay Cat
Bombay Cat British Longhair
British Longhair British Shorthair
British Shorthair Burmese Cat
Burmese Cat Devon Rex
Devon Rex Exotic Shorthair
Exotic Shorthair Himalayan Cat
Himalayan Cat Maine Coon
Maine Coon Oriental Shorthair
Oriental Shorthair Persian Cats
Persian Cats Ragdoll
Ragdoll Scottish Fold
Scottish Fold Siamese Cat
Siamese Cat Siberian Cat
Siberian Cat Sphynx Cat
Sphynx Cat