Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in sheep and goats manifests as vesicles on the feet, mouth, and udders, causing reduced productivity, weight loss, and lameness. Young animals may face high mortality. The disease has economic repercussions, impacting trade and requiring vaccination, bio-security measures, and prompt reporting for effective control.
Common causes of FMD in Sheep and Goat
-
Viral Transmission
Highly contagious FMD virus spreads through direct contact, contaminated equipment, and the environment.
-
Poor Bio-security
Inadequate measures, like insufficient quarantine, contribute to virus introduction and spread within flocks/herds.
-
Global Trade and Movement
Movement of infected animals or contaminated products across borders increases the risk of FMD transmission.
-
Lack of Vaccination
Failure to implement routine vaccination leaves sheep and goats susceptible to FMD infection.
Tips for Prevention of FMD problem in Sheep & Goat
Preventing Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in sheep and goats involves strict bio-security with quarantine measures, adherence to vaccination schedules, controlled animal movement, and maintaining environmental hygiene. These practices collectively reduce the risk of FMD outbreaks and contribute to the overall health of the flock or herd.
Symptoms of FMD in Sheep & Goat
-
Vesicles
The development of vesicles (fluid-filled blisters) on the feet, mouth, and udders.
-
Lameness
Difficulty in walking due to painful vesicles on the feet.
-
Reduced Feed Intake
Infected animals may show a decrease in appetite, leading to reduced feed intake.
-
Fever
An increase in body temperature is a common symptom of FMD.
-
Salivation
Excessive salivation due to painful mouth vesicles.
-
Weight Loss
Infected animals may experience weight loss as a result of reduced feed consumption.
-
Reduced Milk Production
Dairy animals may exhibit a significant decline in milk production.
-
Lethargy
Infected sheep and goats often appear lethargic and less active than usual.
-
High Mortality in Young Animals
FMD can be severe in young animals, leading to a higher mortality rate.
-
Spread to Other Cloven-Hoofed Animals
Sheep and goats can transmit the virus to other susceptible animals, exacerbating the risk of a broader outbreak.
Trusted by Veterinarians
“As a veterinarian, I am thrilled to endorse Dr. Goel Vet Pharma’s homeopathic products for our furry friends. Their commitment to advancing homeopathic veterinary medicine is evident in the exceptional quality of their products. The innovative solutions they provide have significantly enhanced our ability to care for our animal patients, ensuring optimal health outcomes. I highly recommend Dr. Goel Vet Pharma’s products to pet parents for their unwavering dedication to the well-being of pet animals and the invaluable support they offer to the veterinary community.”
– Dr. Sakshi Sharma (B.V.sc. & A.H. M.V.Sc , NET)
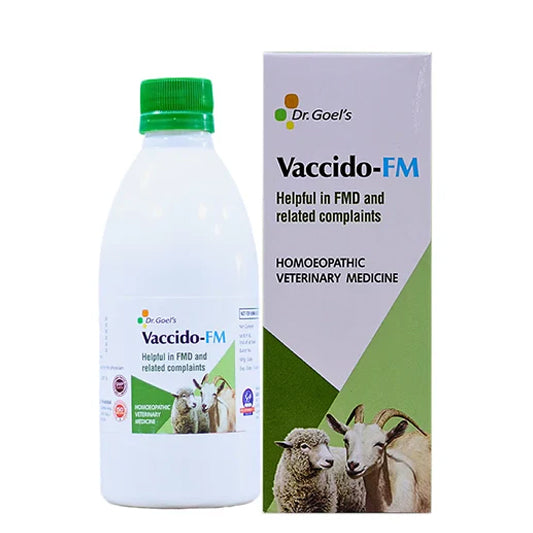
Treat your Sheep and Goat from FMD problem with Dr. Goel’s Vaccido-FM
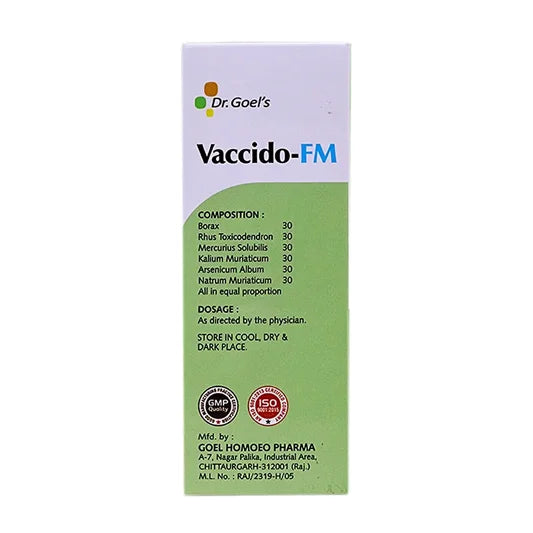
VACCIDO-FM is Homeopathic Veterinary Medicine for Sheep and Goat. It is very helpful in FMD and Related Complaints of FMD.