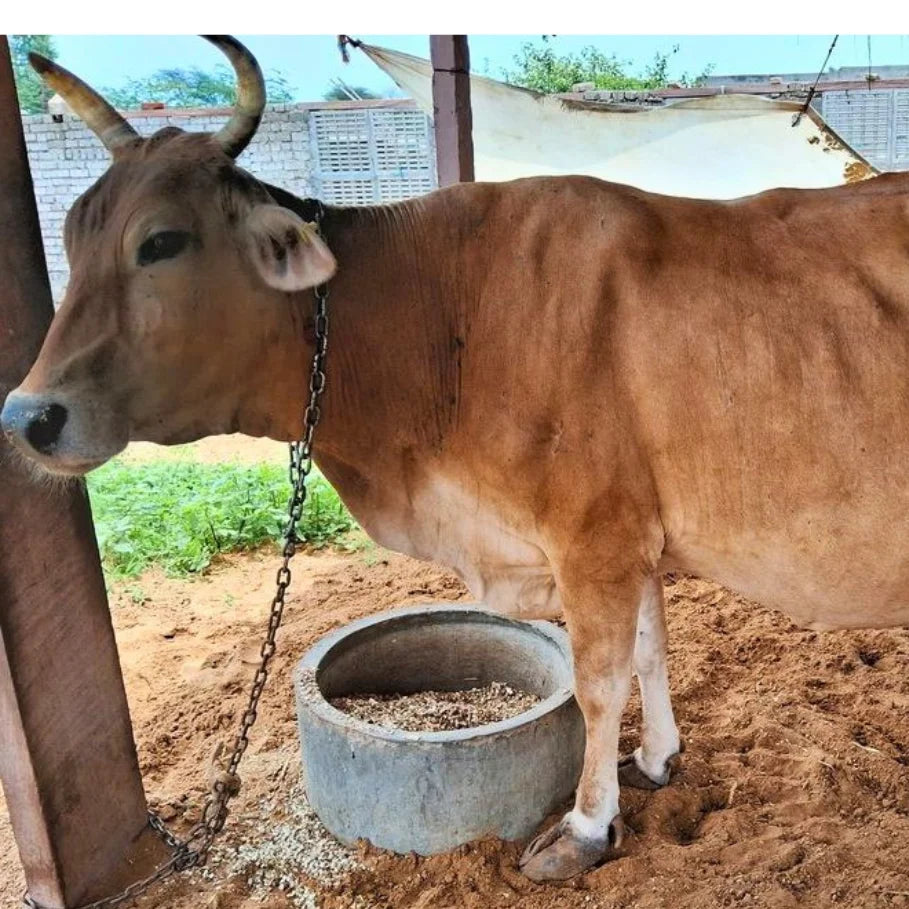
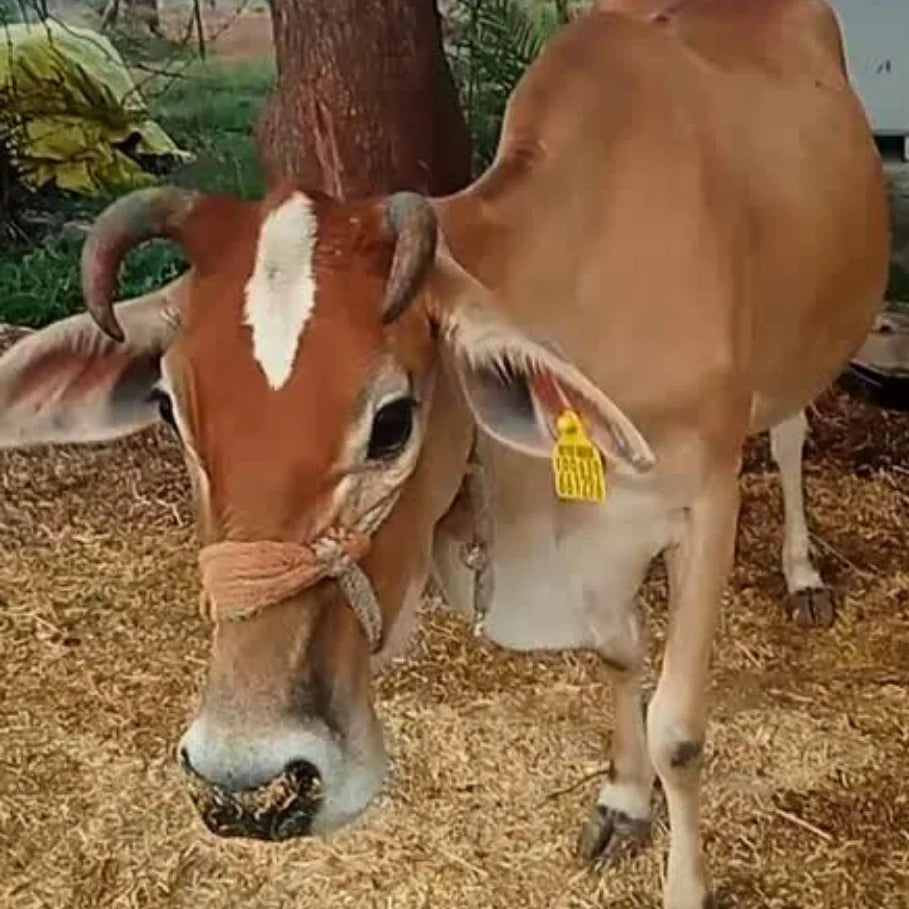
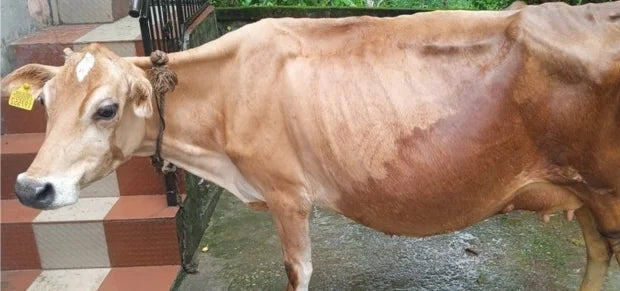


Kankrej cow
| Lifespan Kankrej cattle typically have alifespan ranging from 15 to 20 years, depending on factors such as care,nutrition, and overall management. |
Origin Originating from the Kankrejregion of Banaskantha district in Gujarat, India, this breed is also foundin neighboring Rajasthan and has been exported to countries like Brazil, whereit's known as Guzerat. |
| Temperature Adaptability Kankrej cattle are well-adapted to hot and arid climates, making them suitable for regions with high temperatures. They possess a notable resistance to heat stress and tick fever. |
Weight Cows: Approximately 430 to 455 kg Bulls: Approximately 550 to 570 kg These weights can vary based onfactors like nutrition and management practices. |
| Colors The coat color of Kankrej cattle varies from silver-grey to iron-grey and steel black. Males often exhibit slightly darker shades on the forequarters, hindquarters, and hump compared to the rest of the body. |
-- |
About the Breed
Kankrej cattle are renowned for their dual-purpose utility:
- Draught Power: They are highly valued as fast and powerful draft animals, making them indispensable for agricultural operations and transportation.
- Milk Production: Kankrej cows are fair milk producers, contributing significantly to dairy farming in their native regions. Distinctive features include a broad forehead, slightly dished face, large pendulous ears, and lyre-shaped horns. The breed's resilience includes resistance to tick fever and a low incidence of contagious diseases like abortion and tuberculosis.
Milk Production
On average, Kankrej cows produce about 1,700 to 1,800 liters of milk per lactation, with a lactation period of approximately 300 days. The milk has a butterfat content of around 4.8%, making it suitable for various dairy products.
Common Problems in Kankrej Cows
While Kankrej cattle are generally hardy, they can encounter certain health issues:
Parasitic Infestations
Despite their resistance, they may still be susceptible to internal parasites, necessitating regular deworming.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Inadequate nutrition can lead to deficiencies, affecting milk production and overall health.
Reproductive Disorders
Improper management can result in reproductive issues, impacting fertility rates.